INSERTION SORT
Insertion sort is another sorting algorithm which sorts the list by shifting elements. It is simple to implement and works efficienty for smaller set of data. It "inserts" the key element in its correct position in the sorted subarray at each iteration.
EXAMPLE
Let us consider a list containing 5 elements i.e. 50,40,30,20,10 to be sorted in ascending order by insertion sort. Since a single element is considered sorted, thus it begins with the second index.At each iteration, a key element is selected such that the elements before key element are sorted.
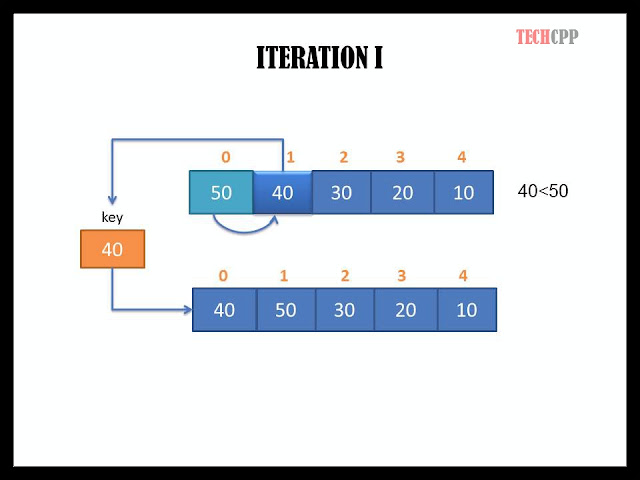
In the first iteration, the element at index 0 is considered as sorted and element at index 1 is selected as key element (Here 40). The key element is stored in a temporary variable and then the shifting of elements is performed. Since 50>40, 50 shifts towards the key element's index making space for the key element. Since minimum index is reached and we are left with no more comparisons, we place the key element at this index.
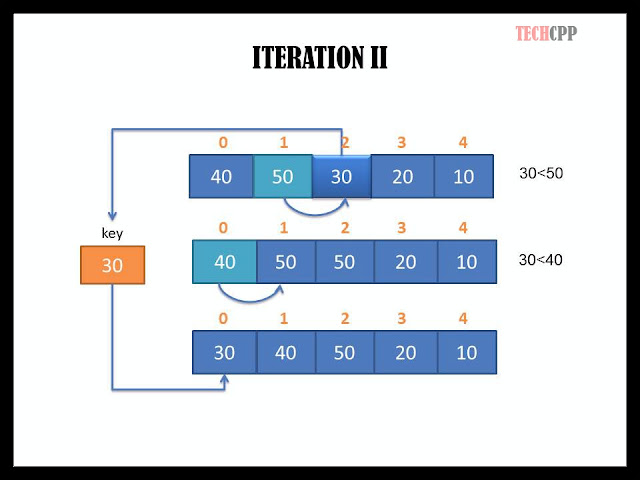
In the second iteration, element at index 2 is selected as the key element (Here 30). Notice that the elements before 30 are already in sorted order, thus we only need to determine the correct position in that sorted subarray for our key element. Since 50 and 40 both are greater than 30, thus both are shifted towards key element's index and the key element(30) is placed in the correct position in that subarray.
In the third iteration, element at index 3 is selected as the key element (Here 20). 20 is again compared with its previous sorted elements for its correct position. 20 being smallest of all its previous elements obtains starting position in the sorted subarray
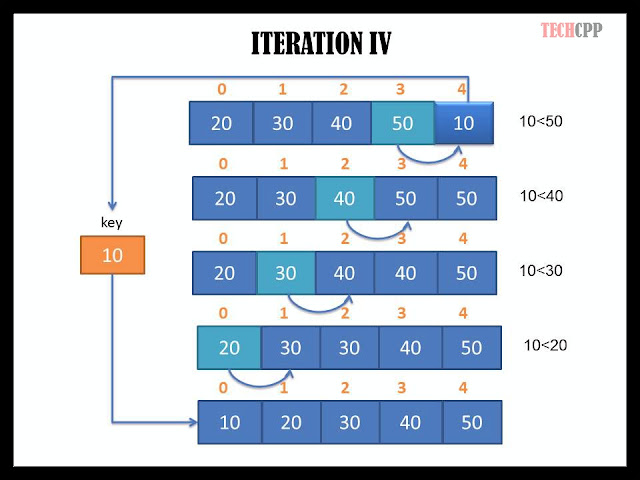
In the last iteration, the sorted subarray consists of n-1 elements of the list and the remaining element is selected as key element. This element is compared with its preceeding elements one by one and acquires its correct position in the array, thus all the elements in the array are sorted.
PROGRAM
// Program to implement insertion sort
#include <iostream>
#define MAX 5
using namespace std;
void insertion_sort(int a[],int size)
{
int i,j,key;
for(i=1;i<size;i++)
{
key=a[i];
j=i-1;
while((key<a[j]) && (j>=0))
{
a[j+1]=a[j];
j--;
}
a[j+1]=key;
}
cout<<"\n\nSORTED ARRAY\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
int i,list[MAX];
cout<<"ENTER ELEMENTS TO BE SORTED\n";
for(i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
cin>>list[i];
}
insertion_sort(list,MAX);
return 0;
}
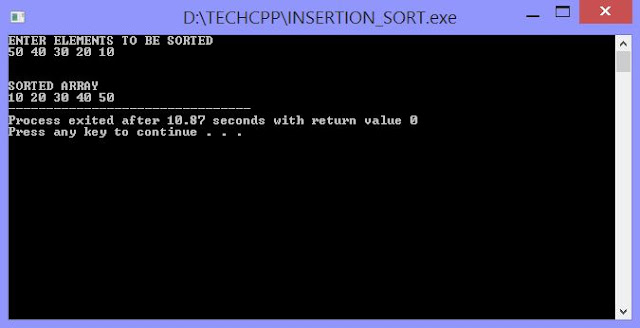
OUTPUT
Insertion sort is another sorting algorithm which sorts the list by shifting elements. It is simple to implement and works efficienty for smaller set of data. It "inserts" the key element in its correct position in the sorted subarray at each iteration.
EXAMPLE
Let us consider a list containing 5 elements i.e. 50,40,30,20,10 to be sorted in ascending order by insertion sort. Since a single element is considered sorted, thus it begins with the second index.At each iteration, a key element is selected such that the elements before key element are sorted.
In the first iteration, the element at index 0 is considered as sorted and element at index 1 is selected as key element (Here 40). The key element is stored in a temporary variable and then the shifting of elements is performed. Since 50>40, 50 shifts towards the key element's index making space for the key element. Since minimum index is reached and we are left with no more comparisons, we place the key element at this index.
In the second iteration, element at index 2 is selected as the key element (Here 30). Notice that the elements before 30 are already in sorted order, thus we only need to determine the correct position in that sorted subarray for our key element. Since 50 and 40 both are greater than 30, thus both are shifted towards key element's index and the key element(30) is placed in the correct position in that subarray.
In the third iteration, element at index 3 is selected as the key element (Here 20). 20 is again compared with its previous sorted elements for its correct position. 20 being smallest of all its previous elements obtains starting position in the sorted subarray
In the last iteration, the sorted subarray consists of n-1 elements of the list and the remaining element is selected as key element. This element is compared with its preceeding elements one by one and acquires its correct position in the array, thus all the elements in the array are sorted.
PROGRAM
// Program to implement insertion sort
#include <iostream>
#define MAX 5
using namespace std;
void insertion_sort(int a[],int size)
{
int i,j,key;
for(i=1;i<size;i++)
{
key=a[i];
j=i-1;
while((key<a[j]) && (j>=0))
{
a[j+1]=a[j];
j--;
}
a[j+1]=key;
}
cout<<"\n\nSORTED ARRAY\n";
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
int i,list[MAX];
cout<<"ENTER ELEMENTS TO BE SORTED\n";
for(i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
cin>>list[i];
}
insertion_sort(list,MAX);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT