UNION
- Union is a user defined variable.
- It consists of more than one non-static data members.
- Union uses a single memory location to hold value of only one of its data members at a time.
- All data members refer to the same location in memory, thus modification of one of the members will affect the value of all of them.
Union can be considered as a container which can contain only one value at a time. The size of union is the size of its greatest data member. For example, if a union consists of integer, double and float data members then the size of union will be the size of double (being the greatest among all members of structure).
PROGRAM
//Program to demonstrate Union type
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
union weight //Definition
{
long long_weight;
long long_weight;
double double_weight;
};
union weight w; //Declaration
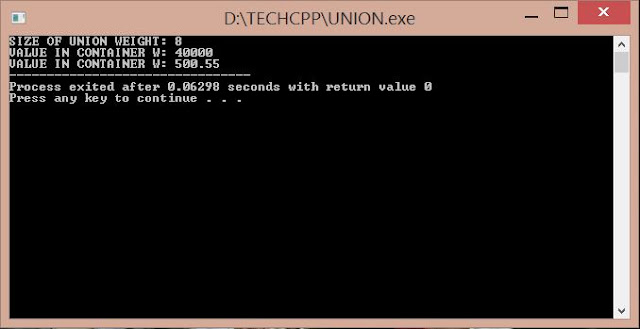
cout<<"SIZE OF UNION WEIGHT: "<<sizeof(w)<<endl;
/* Size of union weight will be the size of double datatype as its size is greater than long datatype */
w.long_weight=40000; //w=500.55 Overwritten
cout<<"VALUE IN CONTAINER W: "<<w.long_weight<<endl;
w.double_weight=500.55; //w=100 Overwritten
cout<<"VALUE IN CONTAINER W: "<<w.double_weight;
return 0;
}
OUTPUT